Abstract
Bile acids (BA) play an important role in the absorption of nutrients and are key regulators of antioxidant and immune homeostasis. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effects of supplementing 0 (CON), 100 (BA100), 200 (BA200), 300 (BA300), and 400 (BA400) mg/kg bile acids on the growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, and immune response of loaches. The serum biochemical analysis results showed that after adding bile acids, the liver injury serum markers (ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH) of loaches decreased. BA mainly affects the lipase activity in the liver and intestines of loaches, but has no significant effect on protease activity. The histological section results showed that supplementing with 100, 200, and 300mg/kg BA increased the number of liver nuclei, improved liver vacuolization, increased intestinal wall muscle thickness, and increased the number of intestinal villi. In addition, BA enhances the antioxidant capacity of loaches by increasing the activities of glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione transferase in their tissues (liver and intestine), as well as the mRNA expression levels of antioxidant related genes (cat, gsh px, sod, and nrf2). At the same time, BA increased the number of serum immune parameters and key immune genes (LYS) (C3, C4, IgM, and LYS), upregulated the mRNA expression levels of anti factor (IL-10) in tissues (liver and viscera), and downregulated the mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1B and TNF-A). In short,Adding BA can improve the liver and intestinal digestive enzyme activity of loaches, enhance antioxidant capacity and immune function, and promote healthy growth of loaches。According to the results of these studies, the optimal supplementation amount of BA in the diet of loach is 200-300mg/kg.

Results
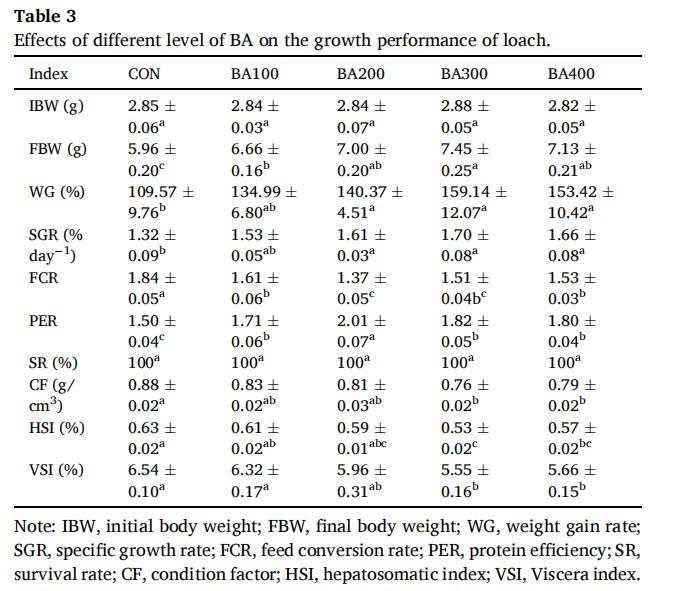
1.生长性能
As shown in Table 3, after an 8-week feeding experiment, BA had a significant effect on the growth and feed utilization of loaches. Compared with the control group,The final body weight FBW and weight gain rate WG of BA200, BA300, and BA400 groupsCompared to growth rateSGR significantly increased (P<0.05), with the highest value observed in the BA300 group; The FCR of each experimental group was significantly lower than that of the control group (P<0.05); The FCR of the BA200 group is the lowest. In all experimental groups, the feed conversion rate and protein efficiency PER were significantly higher than those in the CON group (P<0.05);The PER of the BA200 group was significantly higher than that of the other groups (P<0.05). there="" was="" no="" significant="" difference="" in="" initial="" body="" weight="" ibw="" and="" survival="" rate="" sr="" among="" all="" groups="" p="">0.05).The levels of fatness CF, organ index VIS, and liver body index HIS showed a decreasing trend in all experimental groups, with BA300 and BA400 groups significantly lower than CON group (P<0.05)。
2. Nutritional components of fish:
As shown in Table 4, compared with the control group, the crude protein levels of BA200, BA300, and BA400 groups were significantly higher than those of the control group (P<0.05), with the highest crude fat content in the BA300 group compared to the CON group (P<0.05), and="" the="" lowest="" in="" ba300="" group.="" there="" was="" no="" significant="" difference="" crude="" ash="" content="" water="" between="" all="" groups="" p="">0.05)

3.Biochemical analysis of liver health:
As shown in Figure 1,After supplementing with BA, the levels of liver injury serum markers AST, ALT, ALP, and LDH all decreased。Among them, the AST and ALP levels in the BA200, BA300, and BA400 groups were significantly lower than those in the CON group and BA100 group (P<0.05), and these two parameters reached their lowest values in the BA300 group (Figure 1A and C). The ALT levels of all treatment groups were significantly lower than those of the CON group (P<0.05), and="" there="" was="" no="" significant="" difference="" between="" the="" treatment="" groups="" p="">0.05). The lowest value appeared in the BA400 group (Figure 1D). The LDH levels in the BA300 and BA400 groups were significantly lower than those in the CON and BA100 groups (P<0.05), with the BA300 group having the lowest value (Figure 1D).
Note: AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase.

4.Immunobiochemical analysis:
As shown in Figure 2,After supplementing with BA, the C3, C4, IgM, and LYS values in the serum of loaches all increased。The peaks of C3, C4, and LYS appeared in the BA300 group, while the peak of IgM appeared in the BA200 group. The levels of C3, IgM, and LYS in the BA200, BA300, and BA400 groups were significantly higher than those in the CON group (P<0.05) (Figure 2A, C, and D). The level of C4 increased in all four experimental groups, but was significantly higher in the BA300 group than in the CON group (P<0.05) (Figure 2B). The C3 and IgM levels in the BA300 group were significantly higher than those in the BA100 and CON groups (P<0.05), but="" there="" was="" no="" significant="" difference="" compared="" to="" the="" ba200="" and="" ba400="" groups="" p="">0.05)

5.Morphological observation of liver and intestine:
As shown in Figures 3A, B, C, D, and E, histological section results indicate that in the 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg BA experimental groups, the number of liver cell nuclei increased and vacuolization improved. Excessive BA (BA400 group) can lead to vacuolization and rupture of liver cells. As shown in Figures 3F, G, H, I, and J, in the experimental groups of 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg BA, the intestinal muscles were thicker, and the intestinal villi were longer, smoother, and flatter.

6.Analysis of liver and intestinal digestive enzymes:
As shown in Figure 4,BA supplementation increased the activity of protease and lipase in the liver and intestines of loaches, while the activity of amylase in the liver and intestines was almost unaffected. Compared with the control group, the protease activity in the liver and intestines of the BA200 and BA300 groups was significantly increased (P<0.05), while the protease activity in the BA400 group slightly decreased (Figure 4A). As shown in Figure 4B, the liver lipase activity of BA200, BA300, and BA400 groups was significantly higher than that of the control group and BA100 group (P<0.05), with the peak appearing in the BA400 group. The intestinal lipase activity in the BA300 and BA400 groups was significantly higher than that in the CON, BA100, and BA200 groups (<0.05), while="" there="" was="" no="" significant="" difference="" between="" the="" ba300="" and="" ba400="" groups="" p="">0.05). The lipase activity in the liver and intestine reached its peak in the BA400 group, followed by the BA300 group. There was no significant difference in amylase activity between the BA supplementation group and the CON group (P>0.05) (Figure 4C).

Conclusion
Appropriate levels of BA can enhance the immune function and antioxidant capacity of loaches, promote liver and intestinal health, and thus improve growth performance. According to current research results, the appropriate amount of BA added to loach feed is 200-300mg/kg. The scientific and rational addition of BA provides a new approach to alleviate liver and intestinal diseases in aquatic animals, and BA is expected to become a comprehensive feed additive for aquatic animals.
Author:Liu H, Zhang X, Li K, et al.
The original:Effects of dietary of bile acid on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, liver and intestinal health and immune function in loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)
Link:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2024.102455
Note: Reproduction is only for sharing and for the purpose of learning and communication. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion.